Straight to the point:
Fibonacci Retracement Levels are:
0.382, 0.500, 0.618 — three the most important levels
Fibonacci retracement levels are used as support and resistance levels.
Fibonacci Extension Levels are:
0.618, 1.000, 1.618 — three the most important levels
Fibonacci extension levels are used as profit taking levels.
So, what we will learn today is how to apply Fibonacci tool and how to interpret results that we see on the screen.
To set up Fibonacci on the chart we need to find out:
1. Is it uptrend or downtrend?
2. Highest and lowest swings in the chart formation (A, B points).
And go with the trend!
So, click on Fibonacci tool from trading platform that you use. Now, as shown on the Figure 1:
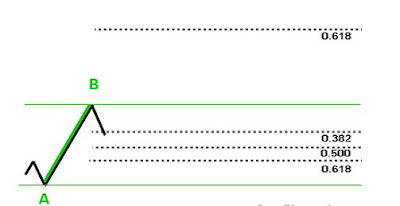
We have an uptrend. A — our lowest swing, B — our highest swing. So, we will look to BUY some lots at the good lowest price and go up with the trend.
Click on A and drag your cursor to B, click. There you go! You must see different lines appeared on your chart. Those lines are called Fibonacci Retracement and Extension Levels.
So, what we are expecting is next: the price should retrace (go down) from point B to some point C, and then continue up in the direction of the trend.
Those three dotted lines (0.618, 0.500, 0.382) at the bottom on our picture shows three Fibonacci retracement levels where we expect the price to take a U-turn and go up again. There we will place our BUY order.
The best situation would be to buy at the lowest level — 0.618 — point C. And on practice the price usually gives us this chance.However, 0.500 is also a good level to place a BUY order.
Well, let's take a look at the progress.
The price has successfully reached the lowest 0.618 point and made a U-turn.
So, now when we have our BUY order placed at desired point C, we would like to set some targets to take our profit in the future. For profit taking levels we use Fibonacci extension levels (0.618, 1.000, 1.618). The most common is 0.618 extension level, but when the price shows good potential to reach next 1.000 or even 1.618 level, you can leave your trade to get that target too.
We will choose 0.618 extension level as our profit target, and according to Figure 2, D is our point for taking profit.
Important note: in this Fibonacci tutorial 0.618 extension level (as well as 1.000, 1.618 levels) are calculated in relation to the point B, which means that B point represents a 0% extension. Some Forex traders like to start counting from point A, then the distance from A to B would be already 100% of the price move. Thus moving further from B would be 1xx.x %.
For example: looking at the last picture, if to start counting from point A, then point D would be a 1.618 Fibonacci extension level or a 161.8% of the price move.